British Business Bank Announces £6.6 bn Boost for UK Innovation
The British Business Bank (BBB), the UK government’s economic development bank headquartered in Sheffield, has been allocated a fresh £6.6 billion in capital as part of the government’s 2025 Spending Review and its new Modern Industrial Strategy. This initiative aims to increase funding capacity from £15.6 billion to £25.6 billion, enabling approximately £2.5 billion in annual investments—an increase of two-thirds.
Two-pronged Investment Focus
The announced capital is structured into two key strands:
- £4 billion - Industrial Strategy Growth Capital
- Targeted investment in eight strategic, growth-driving sectors: advanced manufacturing, clean energy, creative industries, defence, digital/tech, financial services, life sciences, and professional/business services.
- Aims to leverage another £12 billion of private capital, bringing the total to roughly £16 billion over four years.
- Designed to bridge scale-up finance gaps, including direct investments of up to £60 million in high-potential companies, anchoring them in the UK.
- Will also support venture ecosystems by backing specialist and emerging fund managers.
- £2.6 billion - Regional and Inclusive Entrepreneurs Fund
- Focus on "anyone, anywhere", supporting entrepreneurs across UK regions, especially in high-growth innovation clusters.
- Includes new £350 million Nations & Regions Investment Funds for East and Southeast England, plus £100 million boosting existing cluster investments.
- Expansion of the Regional Angels Programme and establishing a new Investor Pathway Capital initiative to nurture diverse and emerging fund managers.
Strategic Goals and Economic Impact
These initiatives are designed to:
- Fill critical gaps in startup and scale-up finance across regions.
- Crowd-in private and institutional investment, with an expected £30 billion of total economic impact (GVA).
- Support the growth and retention of high-potential companies across key UK sectors.
- Develop a resilient finance ecosystem by supporting diverse and specialist managers.
BBB CEO Louis Taylor emphasised the bank’s catalytic role: “Using our market expertise and reach, we have a critical role to play in supporting smaller businesses… no matter what their background or where they are located”.
Building on Momentum
This move builds on BBB's decade-long track record: over £17 billion delivered to nearly 64,000 small businesses via core programmes, plus oversight of £80 billion in COVID-era finance support. It positions the bank to anchor future "star" businesses and rebalance regional inequalities.
What This Means for UK SMEs & Innovators
- Access to larger, tailored equity and debt capital, especially for scale‑ups and deep‑tech firms.
- Enhanced regional funding options, reducing dependence on London‑centric finance.
- Backing for diverse fund managers, improving chances for under-represented entrepreneurs.
- A stable, long-term investment framework built to withstand economic cycles.
UK Unveils £86 Billion Boost to Science & Tech
The UK government has pledged a transformative £86 billion to bolster science, research, and technology over the next four years, reaching £22.5 billion annually by 2029/30. The announcement, part of a broader “Plan for Change,” was made ahead of the 2025 Spending Review and represents a major leap toward establishing the UK as a global leader in innovation.
Key highlights:
• £86 billion to fund everything from new drug treatments and longer lasting batteries to new AI breakthroughs to generate billions for the UK economy and drive the UK government’s “Plan for Change”.
• includes up to £500 million for regions across the UK, with local leaders part of decision making.
• announcement comes ahead of the Spending Review, where the Chancellor will make clear that investing in Britain’s renewal will deliver change for working people and their communities.
Key Objectives
Fuel economic growth: Every £1 of R&D spending is expected to generate up to £7 in economic benefits, stimulate private investment, and support around 3 million jobs.
Boost regional innovation: A dedicated £500 million Local Innovation Partnerships Fund will empower local leaders to direct investment toward their region’s strengths.
The government’s regional focus acknowledges that innovation is strongest when aligned with local ecosystems with targeted investment across sectors such as:
• Liverpool will leverage its life-sciences hub to accelerate new drug development.
• South Wales - home to the UK’s largest semiconductor cluster, will receive funding to develop chips for mobile devices and electric vehicles.
• Northern Ireland stands to gain through enhanced defence technology capabilities.
Each of the seven Mayoral Strategic Authorities in England, including Greater Manchester, West Midlands, South Yorkshire, West Yorkshire, Liverpool City Region, Northeast, and Greater London will receive at least £30 million. Devolved governments in Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland, as well as other UK areas, may compete for additional funds.
Spotlight on Local Innovation Partnerships
This funding builds on successful pilots like Greater Manchester’s AI-powered diagnostic accelerator, which speeds up and reduces the cost of detecting liver, heart, and lung disease, and the West Midlands’ Moonbility platform, using AI to model transport disruption and assist passengers. The Local Innovation Partnerships Fund marks an enduring push toward democratising access to R&D.
Chancellor Rachel Reeves described the initiative as critical to “investing in Britain’s renewal to create jobs, protect our security against foreign threats, and make working families better off”. Science and Technology Secretary, Peter Kyle, emphasised that R&D underpins breakthroughs, from longer-living technologies to climate-fighting innovations, and aims to enhance quality of life throughout the UK.
Policy Alignment & Spending Review Context
The infusion is part of a larger Spending Review package: the Chancellor will unveil £113 billion in new capital investment in housing, transport, and energy, following her modifications to debt rules. These investments align with the government’s shift to empower regional spending via reforms to the Treasury’s “Green Book,” facilitating more strategic, place-based investment.
Universities UK welcomed the announcement. CEO Vivienne Stern praised the plan as “a smart investment” with the potential to spur long‑term growth nationwide:
“The UK has a real opportunity to sow the seeds of long-term growth… from Swansea to Aberdeen, from Barrow to Plymouth.”
Mayor Richard Parker of the West Midlands affirmed the plan would help regions “turn our potential into progress” by supporting clean energy, life sciences, AI, and manufacturing. Northeast Mayor Kim McGuinness said the investment would bolster established industries like automotive and green energy, while enabling growth in space and AI sectors.
Academic and think‑tank concerns highlight the need for an integrated, long-term strategy. Critics argue the UK must address skills development, enterprise diffusion, international recruitment, and commercialisation pathways to maximise returns.
UK in the Global R&D Landscape
With annual R&D spending to reach approximately £22.5 billion, up from present levels, the UK is narrowing the gap with global peers. The NIHR, France’s CNRS, Germany’s DFG, and the US’s NIH are all drawing international talent and investment. In contrast, this commitment gives the UK a competitive edge, reinforcing its position as a leading location for innovation. Broader impacts include:
1. Economic Growth & Jobs: Widespread benefits across healthcare, manufacturing, transport, energy, and digital sectors.
2. Improved UK Resilience: By decentralising innovation and supporting national security needs.
3. R&D Ecosystem Strengthening: Boosting universities, research councils, SMEs, and large-scale industry collaborations.
4. Commercial Translation: Sustained success depends on converting research into business ventures and products.
5. Inclusive Innovation: Gaining equitable access for underserved regions and diverse talent will be critical.
Looking Ahead
The £86 billion R&D funding represents a historic investment in UK science, technology, and regional empowerment. It promises to fuel job creation, advance innovation, and reinforce national resilience. But unlocking its full potential will require nurturing collaboration across government, academia, and industry, backed by efficient implementation and long-term strategic planning.
Success will hinge on:
• Effective regional partnerships.
• Stronger infrastructure and talent pipelines.
• Incentives for commercialisation.
• Inclusive access across the UK.
With Chancellor Reeves’ Spending Review due today (10th June 2025) and the “Green Book” reforms taking shape, the world will watch: this investment is more than a funding surge, it’s a bold declaration of the UK’s future in global science and innovation.
UK R&D Budgets for 2025–26 Announced
In April 2025, the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology (DSIT) announced a substantial allocation of £13.9 billion for research and development (R&D) for the fiscal year 2025–2026. Of this, UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) is set to receive £8.811 billion, emphasising the UK government's commitment to bolstering the UK's position as a global leader in science and innovation. Within UKRI's allocation, Innovate UK, the agency responsible for driving business-led innovation, has been granted £948 million. While this significant funding boost is welcomed, its effective deployment is crucial, especially in light of recent evaluations of Innovate UK's support mechanisms for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Substantial Investment Reflects Government Priorities
The government's decision to allocate £13.9 billion to DSIT's R&D budget reflects a strategic emphasis on innovation as a catalyst for economic growth and societal advancement. This investment is expected to stimulate private sector contributions, with each pound of public R&D funding anticipated to leverage an additional £2 of private investment over time. Such financial commitments are designed to support the government's five national missions and the eight growth sectors outlined in the modern Industrial Strategy. These include:
- advanced manufacturing
- clean energy industries
- creative industries
- defence
- digital and technologies
- financial services
- life sciences
- professional and business services
Innovate UK's allocation of £948 million is intended to support a variety of initiatives, including collaborative R&D projects, support for startups and SMEs, and the development of regional innovation clusters.
Addressing Challenges in SME Support
Despite the increased funding, Innovate UK faces challenges in effectively supporting SMEs. Earlier this year, the agency temporarily halted its Smart Grants programme to conduct a comprehensive review aimed at enhancing support for SMEs. The pause was prompted by concerns over oversubscription and low success rates, with some reports indicating success rates as low as 2%. This situation led to significant resource expenditure by applicants and highlighted the need for a more efficient and targeted funding approach.
Innovate UK's review aims to develop a more tailored support package that prioritises businesses with high growth potential and streamlines the application process. This initiative aligns with governmental objectives to focus public spending on companies poised for scaling and job creation.
Ensuring Effective Allocation and Implementation
While the increased funding for Innovate UK is a positive development, its impact will be determined by the effectiveness of its deployment. Innovate UK must address the issues identified in its recent review to ensure that the substantial financial resources translate into tangible benefits for SMEs and the broader economy. This includes refining grant programmes to improve accessibility and success rates, reducing bureaucratic hurdles, and ensuring that support is directed toward businesses with the capacity to scale and innovate.
Moreover, Innovate UK should focus on fostering strong regional innovation ecosystems, supporting the development of clusters that can drive local economic growth and contribute to the national economy. By addressing these areas, Innovate UK can maximise the return on investment from the increased funding and fulfil its mandate to drive business-led innovation in the UK.
EC Invests €1.3B in Digital Europe Programme
On 28th March 2025, the European Commission announced a significant investment of €1.3 billion aimed at bolstering Europe's capabilities in artificial intelligence (AI), cybersecurity, and digital skills. This funding is part of the Digital Europe Programme's work plan for 2025 to 2027, highlighting the EU's commitment to enhancing its technological sovereignty and accelerating digital transformation across member states.
Note to reader: The United Kingdom is not currently associated with the European Union’s Digital Europe Programme following Brexit. This means UK-based organisations are not eligible to apply for or receive funding through the programme. If you are based in the UK, this article is for information purposes only.
Strategic Focus Areas
The allocated funds will be directed toward several key areas:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Deployment and Adoption: The initiative aims to facilitate the integration of AI technologies into both businesses and public administrations, promoting innovation and efficiency.
- Cloud and Data Infrastructure: Investments will support the development of robust cloud services and data infrastructures, ensuring secure and efficient data management and accessibility.
- Cyber Resilience: Enhancing cybersecurity measures is a priority to protect digital assets and infrastructures from evolving cyber threats.
- Digital Skills Development: The programme emphasises the importance of equipping citizens with the necessary digital skills to thrive in an increasingly digital economy.
Implementation and Accessibility
The European Commission plans to roll out calls for proposals starting in April 2025, with additional opportunities expected throughout the year. These calls will be accessible to businesses, public administrations, and other entities from EU Member States, EFTA/EEA countries, and nations associated with the Digital Europe Programme.
Interested parties can find detailed information on open calls and application procedures on the Digital Europe website.
Alignment with Broader EU Digital Strategies
This investment aligns with the EU's broader digital strategies, including the 2030 Digital Compass, which outlines Europe's digital ambitions for the next decade. By focusing on critical areas such as AI, cybersecurity, and digital skills, the EU aims to position itself as a leader in the global digital landscape.
Henna Virkkunen, the European Commission's digital chief, emphasised the importance of this initiative, stating, "Securing European tech sovereignty starts with investing in advanced technologies and in making it possible for people to improve their digital competences."
Expected Impact
The €1.3 billion investment is anticipated to have a transformative impact on Europe's digital ecosystem by:
- Driving Innovation: Facilitating the development and adoption of cutting-edge AI technologies across various sectors.
- Enhancing Security: Strengthening cybersecurity frameworks to protect critical infrastructures and data.
- Building a Skilled Workforce: Providing citizens with the digital skills necessary to participate effectively in the digital economy.
- Fostering Economic Growth: Enabling businesses, especially SMEs, to leverage digital technologies for increased competitiveness and market expansion.
This strategic investment reflects the EU's commitment to creating a resilient, inclusive, and forward-looking digital environment that benefits all its citizens and positions Europe at the forefront of global technological advancements.
New CEO of UKRI Appointed
A Distinguished Career in Fusion Research
Sir Ian Chapman brings a wealth of experience to his new role, having served as the CEO of the UK Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) since October 2016. His tenure at UKAEA was marked by significant advancements in fusion energy research, positioning the UK as a global leader in this domain. Under his leadership, the organisation transitioned from a focus on deep research and development (R&D) to undertaking major infrastructure projects, including the design and construction of a prototype fusion power plant. This shift not only advanced scientific understanding but also stimulated inward investment, economic growth, and the development of a skilled workforce and supply chain.
Academic and Professional Accolades
Sir Ian's academic journey began at Durham University, where he earned an MSc in Mathematics and Physics in 2004. He pursued doctoral studies at Imperial College London, focusing on plasma physics within tokamak fusion devices, and received his PhD in 2008. His research contributions have been recognized with numerous international awards, including the Institute of Physics' Clifford Paterson Medal and Prize in 2013 and the European Physical Society's Early Career Prize in 2014. In 2022, he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Academy of Engineering, followed by his election as a Fellow of the Royal Society in 2023. His services to global fusion energy were further honoured with a knighthood in the 2023 New Year Honours.
UKRI's Role in Driving Economic Growth
UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) is the UK's principal public research funding body, with an annual budget of £9 billion. It plays a pivotal role in the UK's research and innovation landscape, supporting thousands of researchers and innovators in developing solutions that enhance lives and drive economic prosperity. The organisation's investments have led to significant achievements, such as backing the development of the Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine and constructing advanced wind turbine test facilities, contributing to the UK's status as a clean energy leader. UKRI has also been instrumental in the UK's artificial intelligence (AI) sector, contributing to the £1 billion public investment in AI research and development, positioning the UK as the third-largest AI market globally.
A Renewed Focus on Economic Impact
Sir Ian's appointment aligns with a refreshed mission for UKRI, placing economic growth at the core of public investment in research and development. Science Minister Lord Vallance emphasised that leveraging the UK's innovative ideas, talent, and facilities is crucial for economic advancement and improving lives nationwide. Sir Ian's leadership is expected to drive ambitious, curiosity-driven research while ensuring that investments yield tangible economic benefits, thereby supporting the government's broader objectives.
Community and Expert Endorsements
The scientific community has warmly welcomed Sir Ian's appointment. Sir Andrew Mackenzie, UKRI Chairman, expressed confidence in Sir Ian's ability to unlock opportunities that improve lives and livelihoods, noting his exceptional research and leadership experience. Similarly, Professor Sir Peter Bruce, Vice-President of the Royal Society, lauded Sir Ian's scientific and leadership credentials, expressing confidence in his ability to oversee UKRI's vital work in the coming years.
Looking Ahead
Sir Ian Chapman will assume leadership of UKRI in the summer of 2025. With a renewed focus on aligning research and innovation with economic growth, UKRI is poised to enhance the UK's position as a global leader in science and technology. Sir Ian's extensive experience and visionary leadership are expected to steer UKRI toward achieving its mission of fostering research excellence that translates into economic prosperity and societal well-being.
Proposal preparation grants for 2024 and 2025 calls
Innovate UK and the British Academy have funding schemes open for Horizon Europe Pump Priming Grants, to enable SMEs, research organisations and universities in the UK build partnerships and develop proposals. If you are planning a submission to a 2024 or 2025 Horizon Europe call, one of these schemes may support the development of your proposal.
Innovate UK Horizon Europe Pump Priming
UK SMEs can apply for a grant of up to £5000 (Ex-VAT) to help them in their preparation for submitting a Horizon Europe proposal for a collaborative opportunity. This could be used to fund attendance at networking events, to contribute to the cost of joining associations and other activities that are solely directed at future Horizon Europe participation. Note that if you have already received an Innovate UK Pump Priming grant you will not be able to apply for another in this round. The closing date for applications is 17th January 2025 and the final date on which claims can be made for payment is 17th February 2025.
British Academy Horizon Europe Pump Priming
Principal Investigators (PIs) at universities and research institutions can apply for a grant of up to £10,000 to help them in their preparations for submitting a Horizon Europe proposal for Pillar 2 of Horizon Europe – Global Challenges and European Industrial Competitiveness. All of the details such as eligibility, closing dates, etc., are published on the British Academy website and any questions about this scheme should be addressed directly to them.
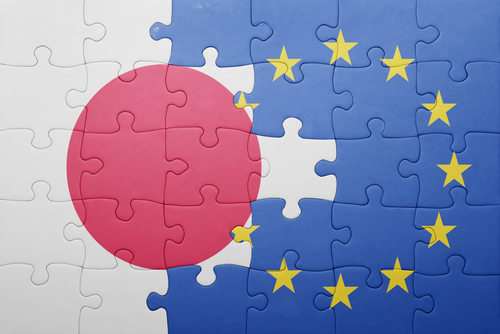
EU and Japan Enter Negotiations for Horizon Europe Association
On 29th November 2024, the European Union (EU) and Japan commenced formal negotiations to integrate Japan into Horizon Europe, the EU's flagship research and innovation programme. This move represents a significant step forward in deepening international scientific collaboration and highlights the global importance of cooperative research in tackling shared challenges. By exploring Japan's association with Horizon Europe, both parties aim to create a mutually beneficial framework for advancing scientific excellence and innovation.
What is Horizon Europe?
Horizon Europe is the EU's most ambitious research and innovation programme to date, with a budget exceeding €95.5 billion for 2021–2027. It succeeds Horizon 2020 and is structured around three key pillars:
- Excellent Science: Supporting top-tier researchers and frontier science through grants and scholarships.
- Global Challenges and European Industrial Competitiveness: Tackling pressing global issues such as climate change, health, and digital transformation.
- Innovative Europe: Boosting Europe's innovation potential by bridging the gap between research and market-ready products or solutions.
As the cornerstone of the EU's research agenda, Horizon Europe facilitates cross-border collaboration, driving breakthroughs that are often unattainable through isolated efforts.
The Context of EU-Japan Cooperation
Japan and the EU share a longstanding history of collaboration in science and technology. This relationship is built on mutual respect and a shared vision of addressing global challenges through innovative solutions. Over the years, their partnership has flourished in areas such as climate action, health sciences, renewable energy, and digital technologies.
Under Horizon 2020, the EU's previous research framework, Japanese organisations actively participated in 176 projects, contributing their expertise to collaborative research efforts. This history sets a strong precedent for Japan's potential association with Horizon Europe.
Why is This Association Significant?
The negotiations are focused on Japan's association with Pillar II of Horizon Europe, which is dedicated to addressing global challenges. By joining this pillar, Japanese researchers and institutions will have the opportunity to:
- Participate in multinational research consortia.
- Lead and coordinate joint projects with EU partners.
- Access funding and resources from the Horizon Europe programme.
This agreement would enable Japan to contribute directly to large-scale, multidisciplinary research initiatives designed to tackle issues like climate change, health crises, digital innovation, and sustainable development.
A Strategic Milestone for Japan and the EU
The association negotiations align with broader strategic objectives for both Japan and the EU.
- For the EU: This move reinforces its commitment to fostering global partnerships in research and innovation, ensuring that Europe remains a hub for scientific excellence. By collaborating with leading global innovators like Japan, the EU strengthens its position in tackling complex global challenges.
- For Japan: Associating with Horizon Europe provides Japanese researchers with access to one of the world's most prestigious and well-funded research platforms. It also allows Japan to integrate more deeply into global research networks, expanding its influence and leveraging international expertise.
Shared Goals: Addressing the Green and Digital Transitions
Iliana Ivanova, the European Commissioner for Innovation, Research, Culture, Education, and Youth, highlighted the importance of this collaboration:
"The opening of the negotiations on the association of Japan to Horizon Europe marks a step change in our cooperation. For both EU and Japan, research and innovation are key to ensuring competitiveness and achieving the green and digital transitions. Together, we will be able to reach them faster and find solutions to the world’s most pressing challenges."
The green transition involves achieving carbon neutrality by mid-century, a goal shared by both Japan and the EU. Collaborative projects in renewable energy, carbon capture, sustainable agriculture, and electric mobility are expected to play a pivotal role in reaching these objectives.
Similarly, the digital transition focuses on advancing artificial intelligence, data science, and cybersecurity. By pooling resources and expertise, Japan and the EU aim to lead in setting global standards for emerging technologies.
What Does Japan Stand to Gain?
Japan's association with Horizon Europe presents numerous advantages:
- Increased Collaboration: Japanese institutions will have greater opportunities to collaborate with European universities, research centres, and industries.
- Access to Funding: Japanese researchers can directly benefit from Horizon Europe's substantial financial resources, enabling them to pursue ambitious projects.
- Global Influence: Participating in EU-led initiatives enhances Japan’s visibility and influence in the global scientific community.
- Innovation Boost: Exposure to diverse perspectives and cutting-edge research can catalyse innovation within Japan's domestic research ecosystem.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential benefits are substantial, several challenges must be addressed during the negotiation process:
- Funding Mechanisms: Determining how Japanese contributions will align with Horizon Europe's funding model.
- Regulatory Alignment: Ensuring that Japan’s research policies and intellectual property laws are compatible with EU standards.
- Administrative Barriers: Streamlining the integration process to facilitate seamless collaboration between Japanese and European researchers.
These challenges highlight the need for careful planning and mutual understanding to make the association successful.
Building a Global Research Ecosystem
The EU's Horizon Europe programme has already established partnerships with other non-EU countries, including Canada, New Zealand, and South Korea. These associations demonstrate the EU’s commitment to fostering a global research ecosystem that transcends geographical boundaries. Japan's inclusion in this network would not only strengthen bilateral ties but also contribute to a more interconnected and collaborative global scientific community.
Autumn Budget: Record £20.4bn R&D investment
In the 2024 Autumn Budget, the UK government announced a landmark investment of £20.4 billion into research and development (R&D) to boost economic growth, tackle national challenges, and establish the UK as a global leader in innovation. This substantial funding demonstrates a commitment to addressing critical areas like healthcare, sustainable energy, digital infrastructure, and technological advancements, aiming to achieve the UK’s “five national missions.” Here’s an overview of the key allocations and expected impacts.
Horizon Europe and Core R&D Budget
A significant portion of the budget secures the UK's full participation in Horizon Europe, the EU's primary research and innovation program. By committing to this association, UK scientists and innovators gain access to an €95 billion fund for collaborative projects, positioning the UK at the heart of global scientific advancements. Additionally, the Department for Science, Innovation, and Technology (DSIT) received a budget increase to £13.9 billion, while core research funding rose to a record £6.1 billion. These increases aim to bolster the UK’s research base and foster innovation across various sectors.
Life Sciences Innovative Manufacturing Fund
The government unveiled a £520 million Life Sciences Innovative Manufacturing Fund (LSIMF) to enhance the UK's capacity for manufacturing critical medical supplies. Starting with an initial £70 million in grants, the LSIMF is expected to unlock up to £1.8 billion in private investment, creating thousands of high-skilled jobs and supporting the healthcare sector’s resilience. This fund aims to strengthen the NHS by ensuring quicker access to innovative treatments, contributing to the UK’s preparedness for future health emergencies.
R&D Missions Programme
A new R&D Missions Programme will initially receive £25 million to address specific national challenges, such as healthcare advancements and clean energy transition. This initiative will foster partnerships with private and third-sector organisations to convert scientific discoveries into practical solutions, enhancing the quality of life and driving forward the UK’s sustainability goals.
Proof of Concept Fund for University Spinouts
To foster innovation from UK universities, the government is investing £40 million over five years in a Proof of Concept Fund. This fund will help researchers transform breakthrough ideas into viable businesses, creating job opportunities and stimulating economic growth. Success stories like Pragmatic Semiconductor and Oxford Nanopore underscore the potential of university spinouts to drive growth, with both companies raising significant investment and creating high-skilled employment in critical sectors.
Innovation Accelerators and Made Smarter Innovation Programs
The budget extends funding for Innovation Accelerators, supporting regional innovation in areas like Glasgow, Greater Manchester, and the West Midlands. These accelerators focus on developing high-potential local industries, with projects like Chemify and the Biochar Cleantech Accelerator attracting millions in private investment. Additionally, the Made Smarter Innovation program will receive £37 million to encourage manufacturers to integrate digital technologies, enhancing productivity and sustainability across UK industries.
Project Gigabit and Shared Rural Network
To improve connectivity, the government will invest £500 million in Project Gigabit and the Shared Rural Network. This funding supports the expansion of high-speed digital infrastructure to underserved regions, with the goal of achieving full gigabit coverage by 2030. Reliable internet access is crucial for businesses and communities across the UK, ensuring equal access to digital resources and fostering regional economic development.
Shared Services Strategy
An £80 million allocation will modernise shared services across nine government departments, streamlining operations for greater efficiency. By updating these systems, the government aims to cut costs and improve services, providing better value for taxpayers.
Barriers to Transformative Technology Adoption
To identify obstacles in adopting transformative technologies, a review led by Chief Scientific Adviser Professor Dame Angela McLean and National Technology Adviser Dr. Dave Smith will assess high-growth sectors. This review seeks to enhance productivity and drive innovation in alignment with the government’s Industrial Strategy, ensuring the UK remains competitive in emerging tech fields.
Reaction from the Scientific Community
This record R&D investment has been met with widespread approval from the scientific community. Royal Society President Sir Adrian Smith commended the government’s recognition of research as a “crucial national asset,” emphasising that protecting the science budget is essential for long-term economic growth. He noted the importance of supporting net-zero initiatives and promoting innovation in sectors like AI to maximise the economic benefits of scientific advancements.
UK’s position on the EU's Research and Innovation Framework Programme
In September 2024, the UK government released a position paper outlining its stance on the EU's upcoming Research and Innovation Framework Programme (FP10). This document highlights the UK's commitment to ongoing collaboration with the EU, focusing on key priorities such as research excellence, global collaboration, security, and the need for reduced administrative burdens. While highlighting the potential benefits of such cooperation, the paper also details the UK’s desire for fair financial contributions and security considerations, setting the stage for future negotiations between the UK and the EU.
Background: The UK's History with EU Research Frameworks
Before delving into the specifics of the UK’s current position, it is essential to understand the history between the UK and the EU in the context of research and innovation collaboration. The EU’s Research and Innovation Framework Programmes, which date back to the 1980s, have always been integral to fostering collaborative research across Europe. Horizon 2020, the predecessor of Horizon Europe, saw the UK as one of the largest beneficiaries and contributors. UK researchers, universities, and businesses often ranked among the top recipients of EU research funding, which allowed them to lead cutting-edge projects and contribute to critical scientific advancements.
However, the UK's decision to leave the EU in 2016 posed significant uncertainties about its future participation in these programs. The post-Brexit Trade and Cooperation Agreement provided a pathway for UK association with Horizon Europe, but the exact terms and conditions were subject to negotiations. The document under review highlights the UK's aspirations to maintain a productive relationship with the EU in the realm of research and innovation, ensuring that Brexit does not lead to scientific isolation.
- Core Objectives of the UK’s Position
The UK government's primary objective in its position on the EU's Research and Innovation Framework Programme is to maintain access to cutting-edge research and innovation networks while safeguarding its own national interests. To achieve this, the document outlines several key goals:
1. Promoting Excellence in Research: The UK emphasises the need for continued participation in programs that prioritise research excellence. The country’s world-leading universities and research institutions have long been central to Europe's research landscape, and the UK aims to retain this role through FP10 (Framework Programme 10). The government stresses that research excellence should remain a cornerstone of EU research programs to ensure that the best minds and institutions can collaborate on solving global challenges.
2. Global Openness and Collaboration: The UK seeks to promote global openness in research. While Europe remains a critical partner, the UK also aspires to expand its research networks to include other countries like the United States, Japan, and Canada. The document advocates for a framework that allows non-EU countries to contribute to and benefit from EU research programs, creating a truly global research ecosystem.
3. Addressing Global Challenges: Tackling issues such as climate change, public health (e.g., pandemic preparedness), and digital transformation are key priorities for the UK. The EU’s Horizon Europe initiative is already aligned with these objectives, and the UK government stresses the importance of continuing to address these global challenges in partnership with the EU and beyond. The position paper highlights that research aimed at solving cross-border problems will be most effective when countries collaborate across geographical boundaries.
4. Security in Research: Given the geopolitical landscape and the increasing importance of data and technology security, the UK insists that any association with EU research programs must consider security issues. This includes protecting sensitive research data, intellectual property, and ensuring that the UK’s national security interests are upheld. The government seeks a balance between open scientific collaboration and safeguarding national security concerns, especially in areas like AI, cybersecurity, and quantum computing.
5. Reducing Administrative Burdens: One of the UK's criticisms of the EU research framework has been its administrative complexity. The UK government advocates for a more streamlined and efficient system that encourages participation from researchers, especially from small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). A reduction in bureaucratic red tape would enable smoother collaboration and a more dynamic research environment.
6. Ensuring Value for Money: Post-Brexit, the UK has faced pressure to demonstrate that any financial contributions to EU research programs deliver tangible benefits for its economy and society. The document emphasises that the UK’s participation in FP10 should be based on a fair contribution model where the benefits to the UK are commensurate with its investment. This is crucial in ensuring public support for continued participation in EU initiatives.
Opportunities and Challenges of UK-EU Research Collaboration
The UK’s position on associating with the EU’s Framework Programme reflects both opportunities and challenges. On the one hand, continued collaboration offers substantial benefits. Horizon Europe provides access to some of the world’s most advanced research infrastructures, databases, and networks. UK scientists, universities, and companies would have the opportunity to collaborate with their EU counterparts on groundbreaking projects that are too large or complex to be undertaken by one country alone.
On the other hand, the relationship is not without challenges. The Brexit process has introduced uncertainties around the legal, financial, and operational frameworks governing UK participation in EU programs. There is also the potential for political friction, especially if either side perceives that the terms of collaboration are not mutually beneficial. The UK government, in its position paper, acknowledges these challenges but maintains that constructive negotiations can overcome them.
The Potential Impact on the UK’s Research Ecosystem
Should the UK secure a favourable association agreement with the EU's Research and Innovation Framework Programme, it stands to benefit in several ways. First and foremost, UK researchers will continue to have access to the EU’s vast research networks and funding opportunities. This would be particularly advantageous for fields such as biomedical research, climate science, and artificial intelligence, where collaboration across borders accelerates innovation.
Moreover, the UK’s commitment to global openness means that the country can continue to foster relationships with non-EU partners while benefiting from its proximity to Europe. This dual approach could strengthen the UK's position as a global research hub, attracting top talent and investment from around the world.
However, if the UK fails to secure an agreement or chooses not to participate, the consequences could be significant. UK institutions would lose access to EU funding and collaborative networks, potentially putting them at a disadvantage compared to their European counterparts. This could lead to a “brain drain,” with top researchers opting to work in countries with better funding opportunities. Furthermore, the UK's research output could suffer if it becomes more difficult to participate in large-scale, multinational research projects.
Navigating the Future of UK-EU Research Relations
The UK’s position on the EU’s Research and Innovation Framework Programme reflects a desire for continued collaboration in a post-Brexit world. By prioritising research excellence, global openness, and a fair financial contribution, the UK aims to remain a central player in European and global research networks. The government's stance highlights the need to balance national interests with the benefits of international cooperation, particularly in tackling global challenges that require collective action.
Moving forward, the success of UK-EU research relations will depend on constructive negotiations that address both the opportunities and challenges of collaboration. If managed effectively, the UK could emerge as a stronger, more globally connected research leader, leveraging its relationships with both the EU and the wider world to drive scientific and technological innovation.
For detailed information on the UK's position, you can access the full document here.
EU Research and Innovation Policy: Key Agendas for Autumn 2024
As Autumn 2024 unfolds, the European Union’s (EU) research and innovation (R&I) sector is entering a period of strategic transformation, marked by new appointments, evolving policies, and critical budgetary discussions. The upcoming months promise significant shifts that will define the future of European competitiveness, defence, and research collaboration. Here's a look at the key points on the EU’s R&I agenda.
New Research Commissioner: Expectations and Priorities
One of the most eagerly anticipated events is the appointment of a new research commissioner. This individual, set to be nominated and quizzed by Members of the European Parliament (MEPs) in the coming months, will significantly influence the EU’s R&I policies for the foreseeable future. The commissioner’s role will be pivotal in guiding the remaining years of Horizon Europe (the EU’s current research and innovation framework) and laying the groundwork for its successor, Framework Programme 10 (FP10).
There is speculation about whether the research portfolio will remain a standalone entity or be merged into a broader portfolio encompassing competitiveness, internal markets, or the economy. As stakeholders wait for the appointment, many are advocating for R&I to stay at the heart of European policy, ensuring continued focus on innovation as a driver of competitiveness.
Defence and Research: The Role of the European Defence Fund
For the first time, defence research is expected to play a more prominent role in EU R&I policy. Ursula von der Leyen, in her campaign for re-election as European Commission President, highlighted defence as a top priority. This includes bolstering the European Defence Fund (EDF), which is designed to support research and development in defence technologies. While the immediate focus remains on urgent defence needs, especially in light of the ongoing situation in Ukraine, long-term plans are also in motion to enhance European defence capabilities through R&D initiatives.
A Clean Industrial Deal: A Pathway to Green Competitiveness
Von der Leyen’s agenda also includes the introduction of a Clean Industrial Deal, which is set to accelerate green technologies across Europe. The goal is to create lead markets in industries such as clean steel and renewable energy, with a particular emphasis on simplifying processes like planning and permitting for green projects. This initiative is part of a broader strategy aimed at positioning the EU as a global leader in sustainable industrial practices.
Although many of these plans are part of von der Leyen’s long-term vision, the Clean Industrial Deal could be instrumental in driving R&I investments in green technologies, aligning the EU’s competitiveness with its environmental goals. This initiative ties in with the broader objectives of Horizon Europe and its successor program, which continue to prioritise sustainability across R&I projects.
FP10: Shaping the Future of European Research
One of the most significant discussions in the R&I community centres around FP10, the next iteration of the EU’s flagship research funding program. An expert group has been convened to assess Horizon Europe’s progress and provide recommendations for FP10. This group, led by former Portuguese research minister Manuel Heitor, is set to deliver its findings in mid-October 2024.
FP10 will likely build on the collaborative research strengths of Horizon Europe, which has been critical in fostering partnerships across Europe. The focus is expected to remain on global challenges, such as climate change, health, and digital transformation, while also incorporating new priorities around defence and industrial competitiveness.
Challenges Ahead: Budget and Policy Debates
While the R&I community welcomes the strategic goals outlined by von der Leyen, several challenges lie ahead. One of the most contentious issues is the budget for Horizon Europe. The European Council has proposed cuts of €400 million to the program for 2025, a move that has been met with resistance from the European Parliament and the research community.
These budgetary discussions are particularly significant as the EU prepares for the next long-term budget cycle, beginning in 2028. Many are concerned that R&I funding could be reduced in favour of other priorities, such as the proposed European Competitiveness Fund. Stakeholders are advocating for a balanced approach that maintains strong support for R&I while addressing Europe’s broader economic and defence needs.
The Role of Competitiveness in Shaping R&I
Competitiveness is at the core of von der Leyen’s policy agenda. In addition to defence and green technologies, she has emphasised the need for Europe to remain competitive on the global stage. This includes fostering innovation through R&I investments, particularly in high-tech sectors like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and biotechnology.
A key component of this strategy is the forthcoming report by former Italian prime minister Mario Draghi, which is expected to provide a roadmap for boosting EU competitiveness. While the report’s release has been delayed, its findings are anticipated to shape much of the EU’s R&I policy going forward.